
Administrative Data Twin
Data Twin acts as a Virtual Clone, embodying the characteristics, behavior, and interactions of its physical counterpart
17
Unlocking data insights for sustainable development goals
30
Empowering districts of Karnataka for sustainable growth
5
Deriving useful insights and transforming years of data for a better tomorrow
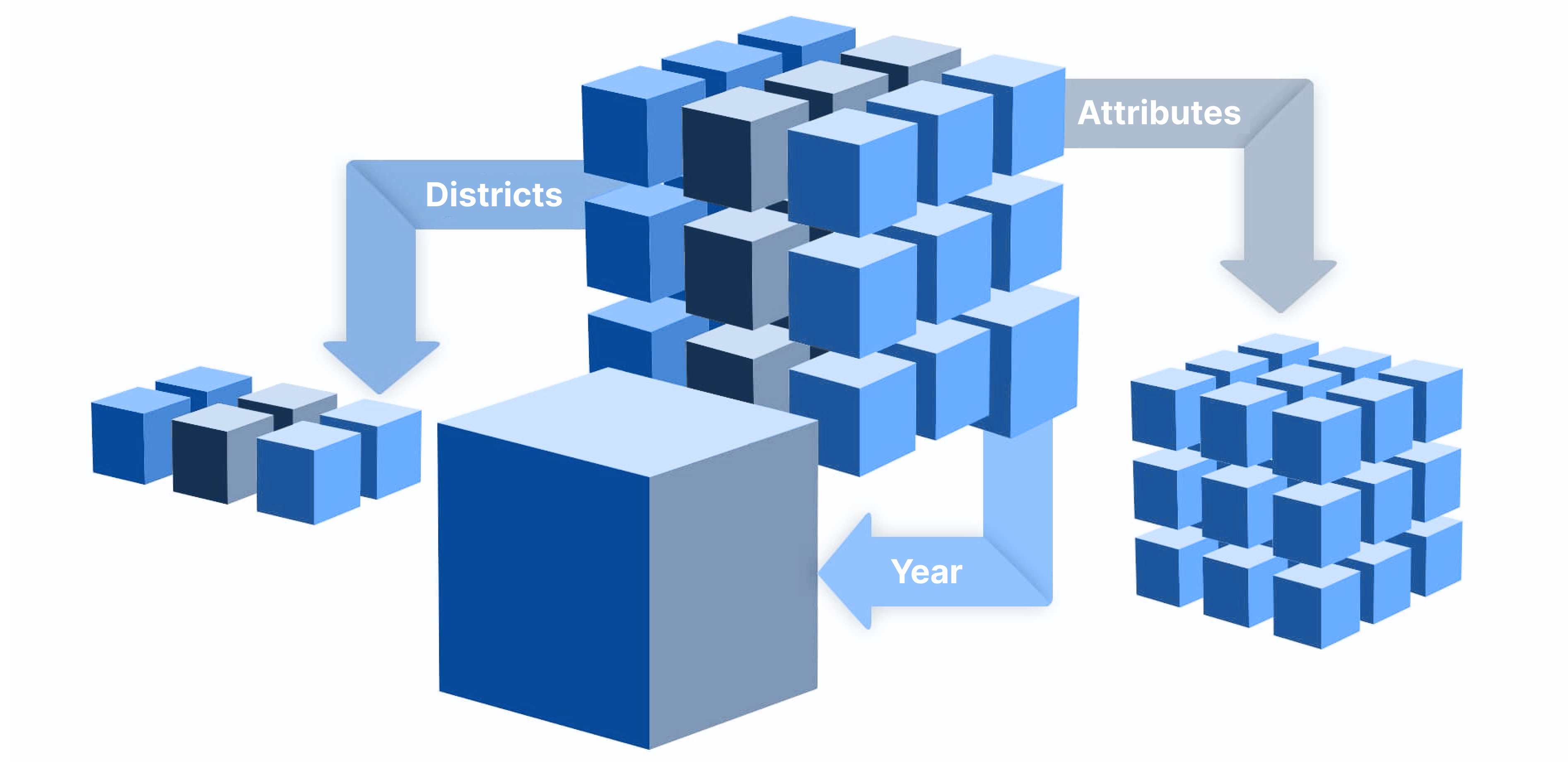
Multidimensional Data
Several Open Government Data (OGD) initiatives have resulted in the availability of open datasets that can be very useful for policy formulation and participatory decision-making. However, integrating these disparate datasets and seamlessly connecting them to all relevant data sources remains a critical challenge. Typically, OGD reflects the performance metrics of geographical units such as states, districts, or villages. Policymakers and data analysts primarily utilize this information for decision-making within specific frameworks like the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In this research, we introduce a Data Warehouse framework over an open dataset provided by the government of the state of Karnataka in India. This framework aims to bridge the gap by enabling a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between data points collected by the OGD processes and SDGs. The proposed data warehouse is constructed using a top-down approach in this research. A fact constellation schema model is proposed to effectively capture information across multiple dimensions, including geographical data, temporal aspects, and various administrative units. The proposed framework is implemented over the OGD dataset called Karnataka at a Glance (KAG), and is equipped to handle OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) queries.
FAQ
Data Twin acts as a virtual clone, embodying the characteristics, behavior, and interactions of its physical counterpart. An administrative data twin serves as a pivotal tool in the area of governance. It functions as a centralized repository, encapsulating comprehensive information about various administrative units, such as villages, taluks, or districts. This digital clone not only mirrors the administrative landscape but also becomes a singular reference point for accessing, managing, and interpreting crucial data.
The motivation behind the Data Twin lies in the fundamental importance of identifying data points and their interconnectedness for effective and sustainable decision making within government entities. The process of prioritizing decisions becomes more streamlined when government agencies adopt a structured approach, often leveraging the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) taxonomy for organizing and analyzing data.
Furthermore, the motivation extends to the administrative level, where government organizations typically follow a departmental structure. This structure aims to enhance data coordination, facilitating more informed and cohesive decision-making processes. In this context, the research is driven by the aspiration to elevate the concept of open data within the administrative organizational framework.
A digital data twin over open data is a virtual representation of real-world entities, constructed from open data sources and applied across various sectors, including smart cities and industrial domains. Acting as a dynamic counterpart to physical systems, digital data twins enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and simulation of their real-world counterparts. In the governmental context, they facilitate access to, visualization of, and insights derived from various entities, aiding in decision-making and resource allocation while promoting prescriptive data analysis. Establishing an administrative data twin involves structured steps: Data Modeling captures real-world entities; Logical Modeling aligns with operational realities; Mapping bridges the logical model to the data model, forming a data twin; and Prescriptive Modeling enhances the data twin with AI-based capabilities, empowering informed decision-making and bridging the gap between data and action.
The future of data twins is poised for exponential growth and innovation, serving as indispensable tools in numerous domains. With advancements in technology, including artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, data twins will evolve into dynamic, real-time replicas of physical entities, enabling predictive analytics, scenario planning, and autonomous decision-making. These digital counterparts will not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive transformative changes across industries, facilitating adaptive responses to complex challenges and unlocking new opportunities for optimization and innovation on a global scale.
